Neuralink's human trials are accelerating

Elon Musk's ventures have consistently captured the world's attention, from revolutionizing electric vehicles with Tesla to propelling space exploration with SpaceX.
Now, Musk's latest foray into the realm of brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) has sparked a fervent debate, with thousands reportedly eager to become a Neuralink volunteer, having a portion of their skull removed and one of Neuralink's brain chips implanted.
Neuralink volunteers allow Elon Musk's brain implant to be tested on them
Elon Musk's brain implant has attracted significant interest, with thousands of people eager to receive the device. The company aims to operate on 11 people next year and over 22,000 by 2030.
Neuralink, co-founded by Musk in 2016, has yet to implant its device in a human but received FDA approval to launch human trials earlier this year. The company is initially targeting people with paralysis in all four limbs due to a spinal cord injury or ALS.
The device, described by Musk as a "Fitbit in your skull," is designed to create a symbiosis between humans and machines, allowing people to send messages or play games using only their thoughts.
Neuralink has conducted 155 implantation surgeries using the robot on a variety of animal test subjects, including pigs and monkeys. The company aims to make the surgery fully autonomous, without human intervention.
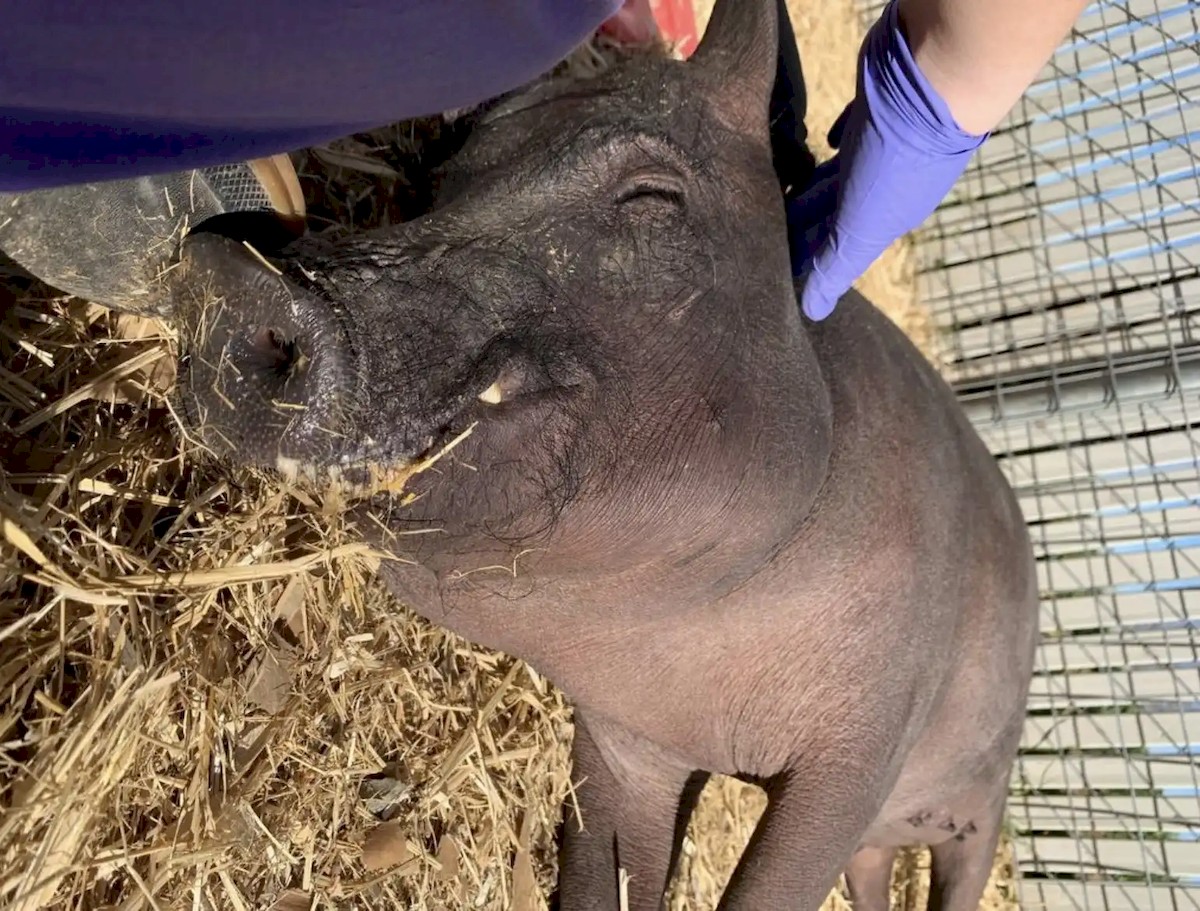
Musk has expressed urgency in developing the technology, citing concerns about competition from other brain-computer startups and the potential threat of unfriendly AI. However, some Neuralink executives have cautioned against rushing the process, emphasizing the need for safety.
Read also: Neuralink receives $280 million funding from a familiar name.
What diseases will Neuralink cure?
Neuralink's brain-computer interface (BCI) technology has the potential to treat a wide range of neurological and motor disorders.
While the company's initial focus is on restoring neurological function in individuals with paralysis, its long-term goals extend to treating a variety of conditions, including:
- Paralysis: Neuralink's BCI could restore motor function in individuals with paralysis caused by spinal cord injuries, strokes, or other neurological damage
- Blindness: The BCI could be used to restore or enhance vision in individuals with retinal degeneration or other vision impairments
- Epilepsy: Neuralink's technology could help to control or prevent seizures in individuals with epilepsy
- Parkinson's disease: The BCI could be used to treat the motor symptoms of Parkinson's disease, such as tremors and rigidity
- Alzheimer's disease: Neuralink's technology could potentially slow or even halt the progression of Alzheimer's disease by restoring lost neural connections
- Mental health disorders: Neuralink's BCI could be used to treat a variety of mental health disorders, such as depression, anxiety, and addiction
Elon Musk's brain implant is still in development, and it is not yet clear whether it will be effective in treating all of these conditions.
What are the potential negative effects of being a Neuralink volunteer?
There are a few potential negative effects of being a Neuralink volunteer.
First, there is the risk of surgery. Any surgery carries risks, including infection, bleeding, and reaction to anesthesia. In the case of Neuralink's surgery, there is also the risk of damage to the brain or spinal cord.
Second, there is the risk of the device malfunctioning. Neuralink's device is still in its early stages of development, and there is always the possibility that it could malfunction. This could lead to a variety of problems, including seizures, paralysis, or even death.
Third, there is the risk of the device being hacked. Neuralink's device is a wireless device, and there is always the possibility that it could be hacked. This could allow a hacker to access your brain data or even control your brain functions.
Advertisement


















“Neuralink has conducted 155 implantation surgeries using the robot on a variety of animal test subjects, including pigs and monkeys. The company aims to make the surgery fully autonomous, without human intervention.”
Great! Autonomous Robots will not only “Hunt and Kill” but also “Select, Kidnap, Operate, and Control” without human intervention.
Except, that is, for the Masters who will program the Robots on just who those robots work for.