Huawei enters the satellite internet arena

The race to provide global internet access has taken a significant leap forward with Huawei's recent testing of its Starlink-like satellite internet service.
The concept of satellite internet has been around for decades, but it has only recently gained traction as a viable alternative to traditional terrestrial-based internet providers. Satellite internet offers several advantages over traditional methods, including the ability to reach remote areas where terrestrial infrastructure is limited or nonexistent.
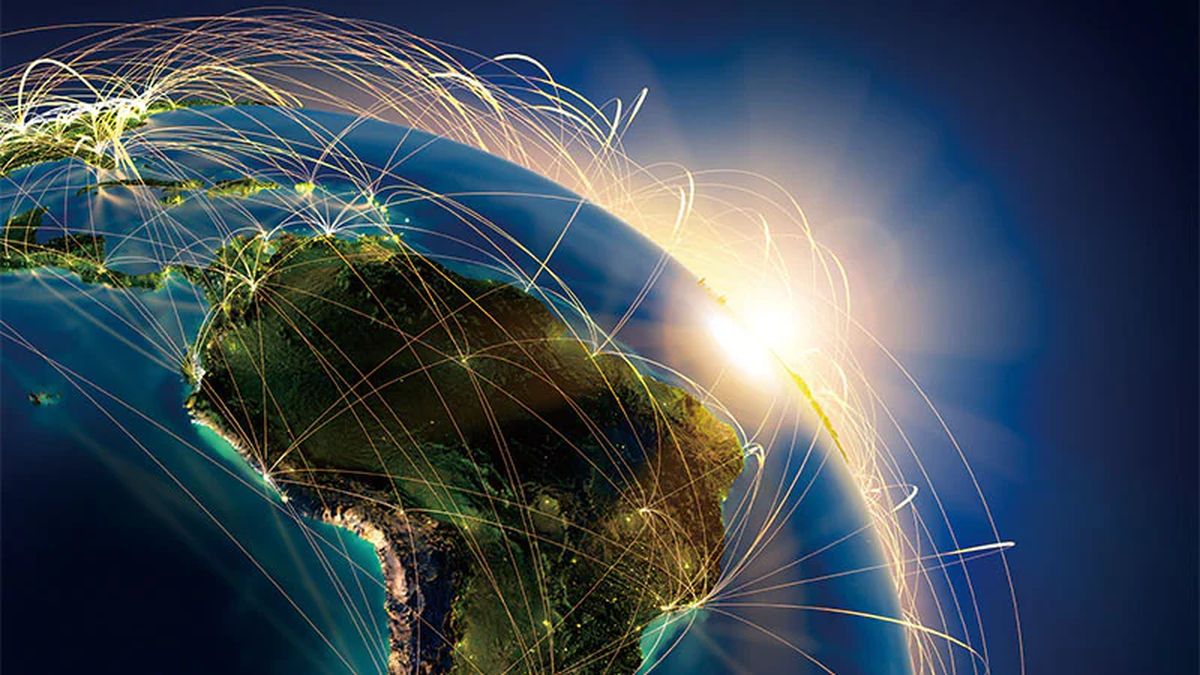
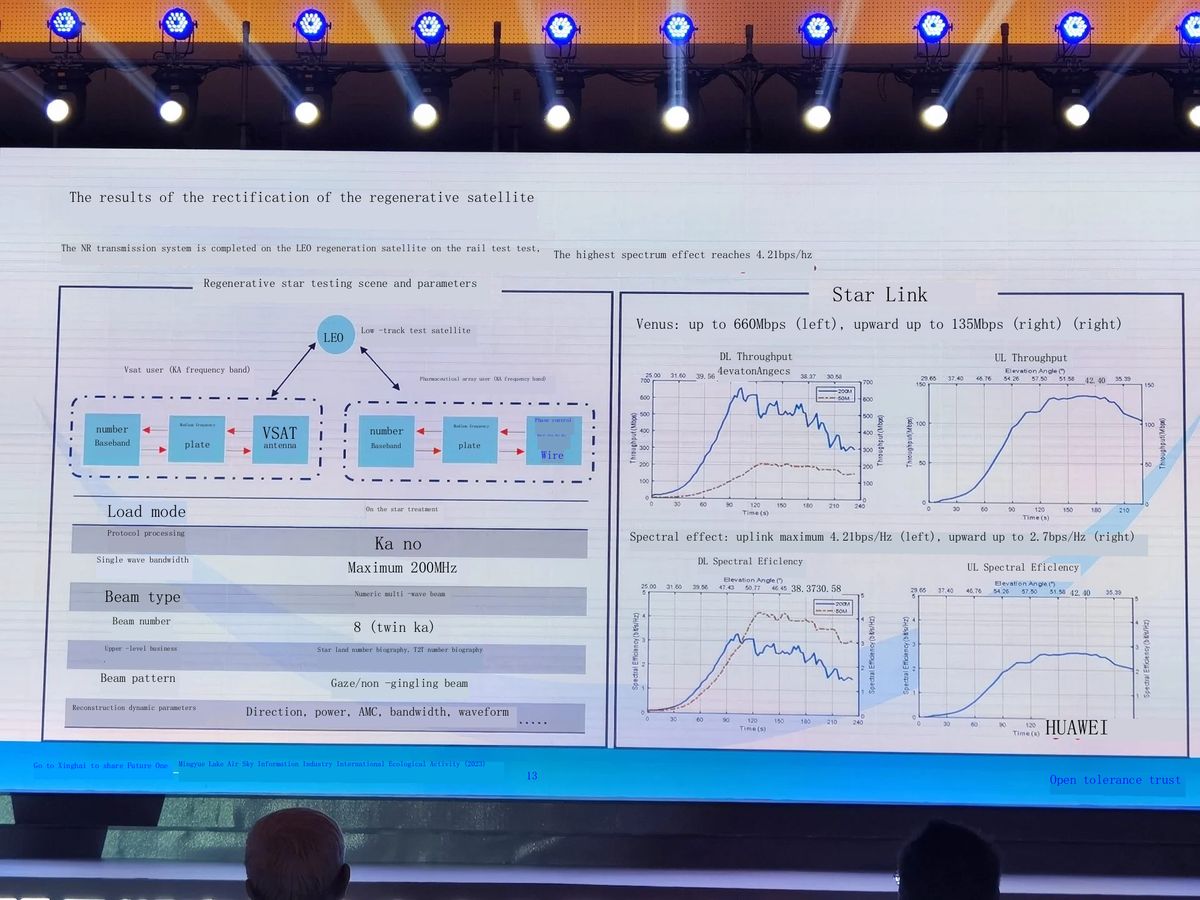
And now, Huawei has achieved download speeds of up to 660 Mbps, a substantial improvement over the current industry standard. This breakthrough marks a major milestone in the development of satellite internet technology and could potentially bring high-speed internet connectivity to underserved regions around the world.
Make some room for Huawei
Huawei's entry into the satellite internet market is significant for several reasons. The company is a global leader in telecommunications technology and has a proven track record of innovation.
Huawei's vast resources and expertise could play a crucial role in accelerating the development of satellite internet and making it more accessible to a wider range of users.
Huawei's recent tests have demonstrated the potential of its satellite internet service to deliver high-speed internet connectivity to even the most remote locations. The company has achieved download speeds of up to 660 Mbps, which is significantly faster than the current industry standard of around 220 Mbps.
This impressive performance suggests that Huawei's satellite internet service could be a viable alternative to traditional terrestrial-based internet providers for many users.
Apart from providing internet access to underserved regions, Huawei's satellite internet service could also be used to support a wide range of other applications, such as backhaul for cellular networks, maritime communications, and aviation connectivity.
The potential applications for satellite internet are vast, and Huawei's technology could play a key role in unlocking these opportunities.

How does satellite internet work?
For those who are unaware of this technology, Satellite internet is a type of internet service that utilizes orbiting satellites to connect users to the global internet. Unlike traditional terrestrial broadband connections, which rely on cables and wires, satellite internet relies on radio waves to transmit data between Earth and space.
The process of satellite internet starts with the user's device sending data to a small satellite dish that is usually mounted on their home or business. This dish, also known as an antenna, receives the data signals and converts them into radio waves that can travel through space.
These radio waves then travel up to a satellite in low-Earth orbit (LEO), which typically sits between 500 and 2,000 kilometers above Earth. The satellite acts as a relay station, receiving the data signals from the user's dish and retransmitting them back down to Earth.
The satellite's signal is then received by a ground station, which can be a large antenna or a network of smaller antennas. The ground station decodes the data signals and sends them back to the internet backbone, which is the network of interconnected fiber-optic cables that make up the global internet infrastructure.
Once the data reaches the internet backbone, it can be routed to any other device connected to the internet, regardless of its location.
Featured image credit: Huawei.
Advertisement