Hard Drive Diagnostics Software GSmartControl
Nothing is worse for a computer user than a hard drive that is nearing the end of its life cycle as hard drive crashes or unreadable sectors could lead to data loss if the user was not prepared for the worst case. But when is the right time to start preparations? Should you start feeling worried when the hard disk begins to make strange noises that seem to grow by the hour? What about the silent Solid State Drives then?
Hard drive diagnostics are essential in analyzing hard drives to have enough time to react when signals indicate a failing hard drive. The only viable option here is to backup all relevant data to other drives or storage devices and disconnect the failing hard drive from the computer.
GSmartControl is a free hard drive diagnostics program for Windows, Mac and Linux that is offered as a portable version, installer and Live CD to suite all work environments and scenarios.
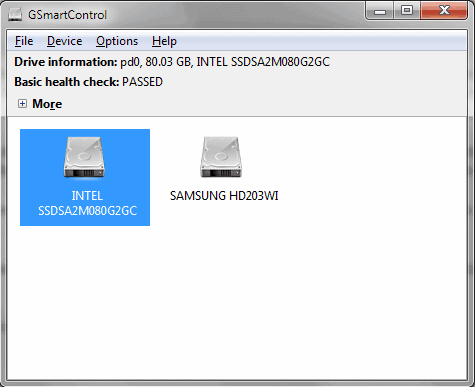
The name implies that the software is only able to analyze hard drives that support S.M.A.R.T., the Self-Monitoring, Analysis, and Reporting Technology, which most modern hard drives support. GSmartControl will automatically scan and display all connected hard drives on startup.
Each hard disk is displayed with a drive icon and name which usually is enough to identify it. Basic drive information are displayed at the top of the screen after a drive has been selected with the mouse. Information displayed there include the drive's capacity and if it did pass the basic health check.
Some users might not see the basic health check information after selecting a drive. This usually means that SMART is either not activated or that the drive is not supporting SMART at all. SMART can be activated by right-clicking a drive and selecting Enable SMART. This will not work if the hard drive is not supporting the SMART technology or if SMART is disabled in the computer bios.
The best option in this case is to reboot the computer and check the BIOS to make sure that SMART is enabled there. If SMART cannot be activated after this it is not supported by the hard drive.
A double-click on any drive will open the Device information, a tabbed window with extensive information about the selected hard drive.
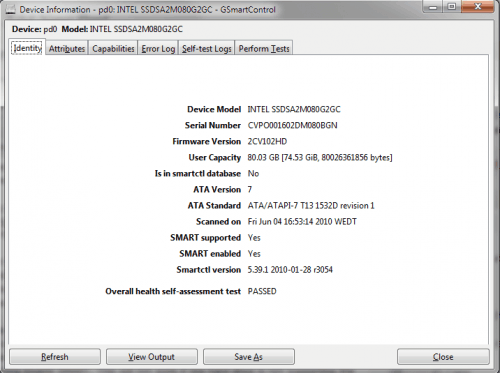
The Identity tab displays important information about the drive. It will list the device model, serial number, firmware, capacity, ATA version, if SMART is supported and enabled and if the overall health self-assessment test has been passed.
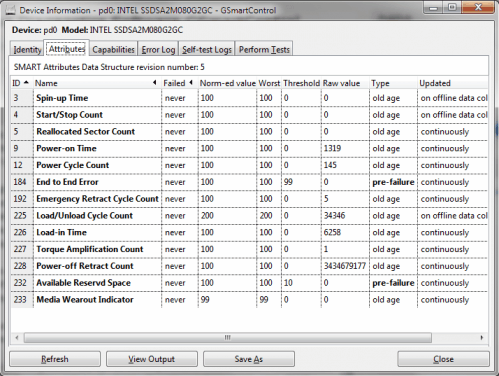
The attributes tab displays SMART attributes data. The important information are listed in the failed column which should show never to indicate a good drive health. Another indicator are the norm-ed value and worst which should not diverge at all for best results.
The Error log tab displays the five most recent errors that the hard drive has encountered. No errors are another indicator of a good drive health.
The Perform Tests tab lists various tests that can be performed. This includes a short self-text, extended self-test and conveyance self-test. It is usually a good idea to begin with the short self-test and execute the extended self-test afterwards.
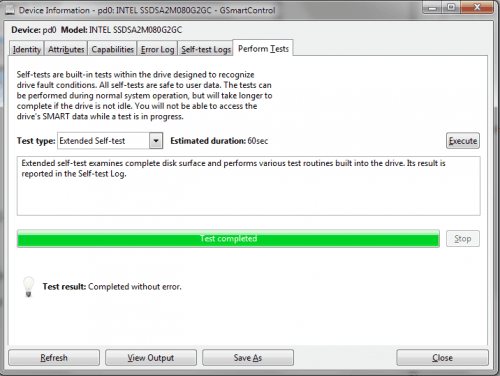
- Short self-test consists of a collection of test routines that have the highest chance of detecting drive problems. Its result is reported in the Self-test Log. Note that this test is in no way comprehensive. Its main purpose is to detect totally damaged drives without running the full surface scan.
Note: On some drives this actually runs several consequent tests, which may cause the program to display the test progress incorrectly. - Extended self-test examines complete disk surface and performs various test routines built into the drive. Its result is reported in the Self-test Log.
- Conveyance self-test is intended to identify damage incurred during transporting of the drive.
A log file is generated for every test that can be viewed by clicking on the View Output button. The log file contains detailed information about the hard drive and a final assessment. Completed without error indicates that the drive is in good health.
GSmartControl comes with an option to perform a self test every few hours. This test is not affecting the performance of the drive or computer system and can be helpful in monitoring a drive's health over time.
The hard drive diagnostics tool can also be executed from the command line. All command line options are explained in the program's help file or by adding -? to the executable.
GSmartControl is a invaluable diagnostics software for hard drives. It's tests and automatic options make it a recommended tool for every system administrator and end user.
Versions for all operating systems are available at the developer's website.
Advertisement













Thanks Martin! It looks like my lone surviving ATA hard drive is near its end.
Free or cheaper? This program is open source. Idiot!
There are a couple of other software offerings that give similar functionality to this but are free or cheaper.
Mind you this does look quite thorough so I may still have a go with it.