Windows 8 Storage Spaces, What You Need To Know
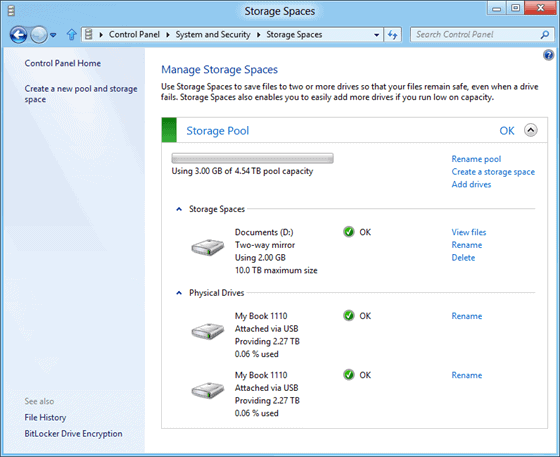
I had to read Microsoft's new post at the Building Windows 8 blog twice to fully understand the Storage Spaces feature the company plans to introduce in the Windows 8 operating system.
Storage Spaces is a new drive virtualization technology. It allows users and admins of the Windows 8 operating system to create drive pools and virtual disks.
Drive Pools combine the storage space of one or multiple hard drives. Drives with different speeds, storage capacities and connections can be combined to a drive pool. A drive letter is assigned to a drive pool so that the operating system and applications may access it directly.
Virtual disks on the other hand behave just like physical disk in most aspects but there are a few exceptions. The device cannot boot from virtual disks but they do support thin provisioning and resiliency to failure which are interesting features and especially so in business environments.
Lets take a closer look at the features. Thin provisioning can be used to assign more storage capacity to a pool than is available at a point in time. The pool itself will only use as much storage space as needed to store the data so that it works similar to the dynamic disk size feature of Virtualbox and other virtualization solutions.
This is different from regular hard drive partitions that always make available a set amount of space on a system. Thin provisioning can increase the storage efficiency of a system. And if storage space runs out it is just a matter of connecting a new hard drive or assigning unused space to the pool to overcome the shortage.
Resiliency through mirroring and parity make sure that data remains available even if a hard drive fails and needs to be replaced. Mirroring basically makes sure that data is available on at least two physical drives so that recovery is possible even if one of the drives fails.
Parity on the other hand saves information "alongside user data within the space" so that data can be reconstructed if a drive fails or if it becomes corrupt. Usenet users may about know the parity concept from par files that often get uploaded besides the actual files so that corrupt files can be reconstructed locally.
Drives can be replaced easily if mirrored or parity spaces has been created. If that is the case the drive can simply be replaced. Storage Spaces will automatically synchronize the data once the drives connects. Synchronization is an automatic feature which can also be triggered manually with the help of the repair command via Powershell.
As far as mirroring goes: The technology supports two-way and three-way mirrors, with the possibility to assign data to specific disks manually.















Do I understand it correctly that just like alcohol 120 this Microsoft Virtual disks use physic letter numbers?
So when you have (like me) already 18 (incl.USB stick/Dvd – & cd drive) letters assigned to a drive , how many virtual disk can I make?
So if I understand this correctly, they decided to bring Drive Extenders from the first Windows Home Server back…
Given that was yanked because it wasn’t ‘ready for business’, wonder if they actually fixed anything or if this is just one of those “We’ll promise it now to build up hype, and quietly drop it before release” features Microsoft sometimes seems to announce for their products.
Well according to Microsoft it is not the same feature, it is for instance better integrated with NTFS.