Canon Quantum dots will allow OLED panels to be produced without the need for rare metals

Canon has made a groundbreaking leap in organic light-emitting diode (OLED) technology by developing innovative materials that eliminate the need for rare metals. This remarkable achievement not only demonstrates Canon's commitment to reducing reliance on major rare metal producers, particularly in China but also sets the stage for stable production without geopolitical risks.
With their sights set on commercializing this breakthrough technology within the next few years, Canon is poised to transform the landscape of high-end displays.
Quantum dots are a game-changing material for OLED panels
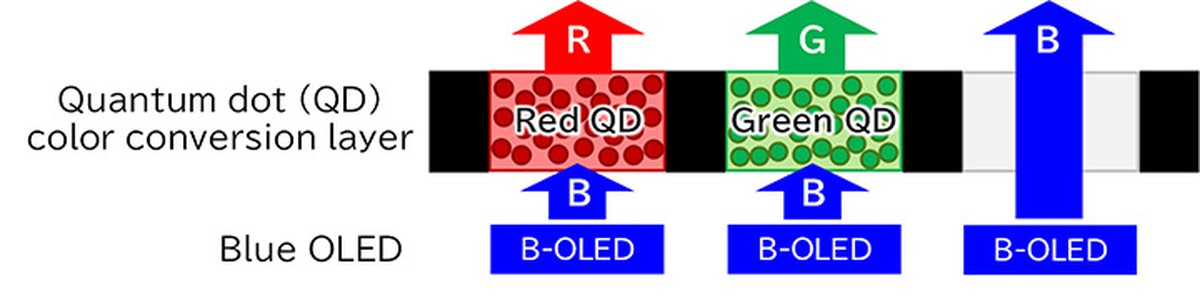
Canon's latest development revolves around the integration of quantum dots (QD), tiny semiconductor particles with a diameter of just 1 nanometer. These remarkable particles emit vibrant and immersive colors when stimulated by light or an electric current.
Quantum dots have already found application in high-end OLED televisions, but Canon's innovation takes it a step further by utilizing a rare metal-free material.

Reducing dependence on rare metals
By opting for the lead as a key component in their quantum dot OLED panels, Canon addresses the growing concerns surrounding the availability of rare metals, particularly indium, which is predominantly sourced from China. Indium phosphide, a compound widely used by Samsung Electronics in mass-produced quantum dot displays, relies heavily on scarce indium reserves.
Canon's approach, on the other hand, capitalizes on lead, an easily procurable resource obtained from recycled materials in urban mines. This not only ensures a more sustainable supply chain but also mitigates geopolitical risks associated with rare metal procurement.
What will quantum dots change?
Canon's expertise in material composition has allowed them to overcome the durability challenge typically associated with using lead instead of indium. By leveraging their knowledge in compounding materials, such as toner and ink for office equipment, Canon has successfully developed a compound that matches the longevity and reliability of indium.
The integration of quantum dots into OLED panels offers numerous advantages, including vivid and evenly bright red and green hues, even under well-lit conditions. Additionally, power consumption is significantly reduced, making these displays approximately one-third more energy-efficient than conventional screens.
The expected impact on the market
The quantum dots market is projected to experience exponential growth, with Global Information forecasting a market value of $21.1 billion by 2027, representing a 4.1-fold increase compared to 2021. Furthermore, Omdia predicts a significant surge in the number of televisions equipped with quantum dots, estimating that it will surpass 22 million units by 2025, accounting for approximately 8% of the total television market.
The introduction of Canon's rare metal-free quantum dot materials holds great promise for reshaping the high-end television market and making advanced display technology more accessible to consumers.
Advertisement