Map your network with Lanmap
This morning I needed a visual representation of my local Lan in order to find out what machines were associated with what IP addresses. For this task I used a tool that has come in handy on a number of occasions. That tool? Lanmap. Lanmap is a command-line only tool available for Ubuntu that will monitor your network and compose a 2D image of your network. This image will include information about your machines as well as packets sent and MAC addresses. The tool is incredibly handy to have around.
I will warn you: The creator of Lanmap has dropped this application in leiu of creating a much more robust Lanmap-2. Unfortunately Lanmap-2 is not complete so Lanmap one will have to be used until 2 is complete. Fortunately Lanmap is still in the Ubuntu repositories so installation is a snap. And once installed, Lanmap is equally as easy to use.
Installing Lanmap
As stated earlier, Lanmap is only available for Ubuntu (and Debian-based) systems. Most likely, if you use apt-get, you can install Lanmap. Of course you don't have to install via command line, but if you want to just issue the command:
sudo apt-get install lanmap
This command will prompt you for a Y or N to install the requirements. Click "y" (no quotes) and hit enter. Lanmap will install quickly and you'll be ready to map.
If you want to install via GUI tool open up your Add/Remove Software utility (found in the Applications menu in GNOME), do a search for "lanmap" (no quotes), select the resulting lanmap entry, and click Apply. Once you "okay" the dependencies the installation will be off and running.
Using Lanmap
Lanmap is a command line tool that generates an image. The structure of the command is:
lanmap -i INTERFACE -r INTERVAL -T IMAGE_TYPE DIRECTORY_TO_STORE_IMAGE
Here are the specifics:
- INTERFACE: The interface you want to use to listen to your network. Typically this will be in the form of eth0. You can use all without using the -i switch to listen on all interfaces.
- INTERVAL: This sets the interval (in seconds) between two consecutive graph generations (default being 60).
- IMAGE_TYPE: The type of image file you want to generate. The only supported types are: png, svg, and gif.
- DIRECTORY_TO_STORE_IMAGE: Where you want to store the image file.
So if I want to scan my network with all interfaces and create a png image I would issue the command:
lanmap all -r 30 -T png ~/

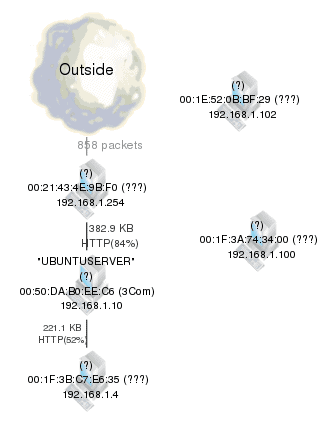
The resulting map (I am currently writing on a far smaller network with machines that are not broadcasting their hostnames. You can see the IP addresses and MAC addresses of course (see Figure 1).
You can see one machine (at IP address 192.168.1.10) is broadcasting as "UBUNTU SERVER", but outside of that, no hostnames are showing up. This is not really a problem at this size of a network. On a larger network I would hope more machines will show up with their hostnames. This, of course, will depend upon your network setup.
Final thoughts
I have used plenty of applications to create network maps that range from too many bells and whistles to too few features. Lanmap ventures close to the latter, but offers just enough features to make it not only useable but useful. Give Lanmap a try, I think you'll find it as helpful a tool for your networking toolkit as I do.
Advertisement













It’s a good software
I prefer to use ProteMac Meter.
It records all internet and network activity and it is very easy to use)
Does my mac adresse change if I upgrade my computer with some other hardware? For example change the graphic card?
No, sir. There will be no changes in MAC address, unless you change or add a network interface card, wireless usb, etc.