TinEye Reverse Image Search Engine

TinEye is a reverse image search engine that enables you to find matching images for an image that you upload to the service.
Reverse image search refers to the concept of searching for duplicate or related images of a specific image on the Internet. The usual image search engines do not offer the feature, all you can do using them is enter a search term and hope for the best. If the image has been renamed, you won't find it this way as they only display images related to the search term in the results.
Reverse image search engines on the other hand take an image that you have, analyze it, and find copies of it on the Internet that look identical or at least similar.
Update: Please note that Google has rolled out a reverse image search option on Google Images recently. You can use it as well to search for an image that you upload or paste as an url.
TinEye
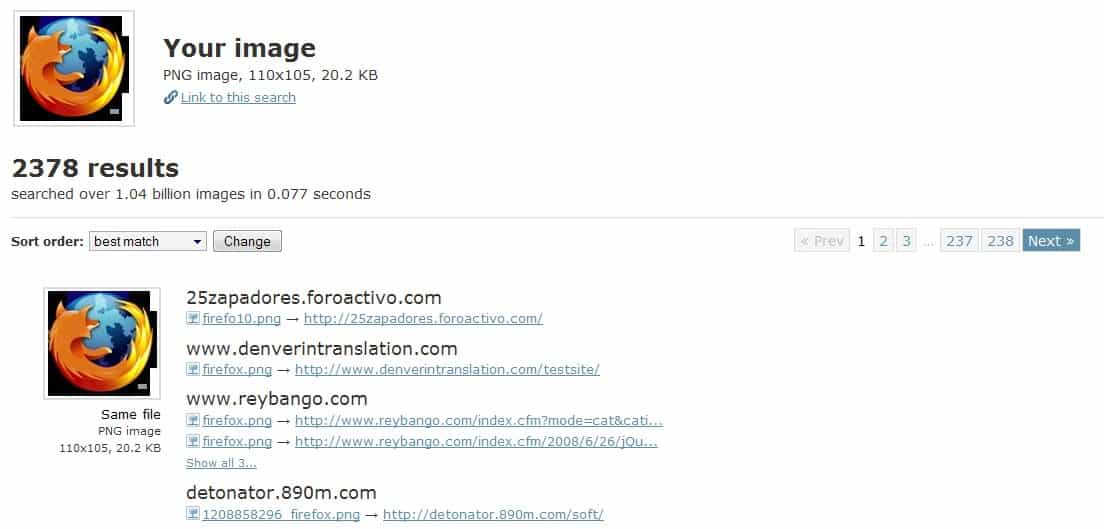
TinEye is a reverse image search engine that accepts images that you upload from the local computer, but also images that you have found on websites by using links.
The second method requires some explanation. It is possible to point the search engine to an url of an image or to point it to a website. Pointing it to a website will retrieve all images located on that website, and it is up to you to select the one that you want used for the reverse image search. Only one image is used either way for the search.
The quality of the results depends a lot on the selected image. TinEye will display the number of related images that it found in its database which it states contains 1.04 5.24 18 billion entries. A quick test for images on Ghacks brought up mixed results. A search for the Firefox logo used on this site returned more than 2000 results while a search for the Ghacks logo returned a handful that were not related at all.
The results show a preview of the images that are returned, information like the resolution and size, and url it was found on. You can click on the compare link displayed there to display the image you ran the search with and the matching image in an overlay on the screen. While they are not displayed side by side, you can click on the switch button to display them on top of each other so to speak.
Different sorting options are provided on the page as well. TinEye selects the best match by default, but you can change that to most changed, biggest image, newest or oldest instead.
TinEye offers an interesting service that might be useful for people who like to check if their images or photos are used on other websites. It might also be interesting for research and other purposes. The service is currently in beta stage.
Update 2: TinEye is no longer in beta. The company behind the product has released browser extensions and bookmarklets that you can make use of to improve the usability of the service.
The browser extensions for instance allow you to right-click on images to run a search for that image using the search engine.
The bookmarklet is compatible with all modern browsers. It sends the url of the active page to TinEye so that you can select one of the images published on it for the search functionality.
Verdict
So what can you use the service for? One interesting application is to find out which other websites have used to one of your images. You can find scraper sites this way or sites that have used the image without proper authorization.
It is also possible to find a larger version of an image, for instance for use as a wallpaper, or similar images to the one that you already have.


















blah, I’ve tried it way more and I’ve always had *some* hits, and there were times I had 200+ hits, so it does work, their database just isn’t very large yet (1 billion images I believe, which sound like a lot, but it really isn’t)
However it does work, and it works splendidly!
I’ve used it numerous times the past… 3-6months and it’s NEVER found a single image.
It is still in beta, one can,t expect much from this service.
Well google’s similar images search only works for pictures that are already visible on the site. You cannot specify an url or upload pictures as far as I see.
What about google’s new “Similar images”?
http://similar-images.googlelabs.com/
Nice article, but was this inspired by all of the talk on Google Similar Images search in Google Labs?