Windows Boot Manager
Many users shy away from installing multiple operating systems on their computer because of problems that can arise in the boot sector. Some operating systems like to replace the existing boot information with their own which would mean that the user would have to find a way to replace or add those boot information again so that all operating systems would show up when booting the computer.
Windows boot manager Boot-US is a universal boot manager that can boot many operating systems properly including all versions of Microsoft Windows from Windows 95 to Windows Server 2008, MS-Dos, Linux, Free BSD, VMWare and several exotic operating systems like Oberon, Novel-DOS or QNX Realtime Plattform.
The boot manager itself can be installed in the MBR (Master Boot Record), the primary partition or on disk. The latter being an excellent way of testing the boot manager before installing it on the hard drive.
Other interesting functions of the Windows boot manager are (Windows because it is a Windows application):
- Support for hard disks up to 2048 GB (2 TB)
- Allows booting beyond the 8 GB limit
- Partitions can be created, deleted, activated and hid
- Password protection for boot manager and configuration program
- Command-line and GUI version
- True hiding of partitions
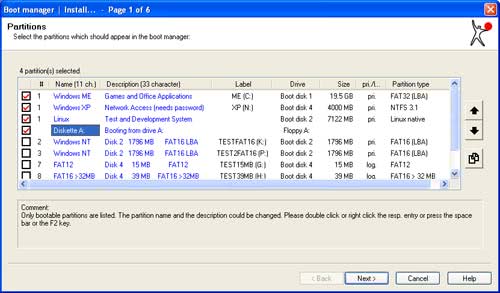
During program start the Windows boot manager is displaying the discovered partitions and the existing operating systems. It is important to make sure that the information that are displayed are correct before installing the boot manager. The user should also consider making backups of the list of partitions and boot sectors to be able to revert back if the installation of the boot manager goes wrong in any way. Those are just precautionary measures.
After that the user should install the boot manager to a floppy disk first if one is installed on the computer system. Most modern computers come without a floppy disk drive. Those users can check out the Copy and run Floppy Boot Disks from USB to add the boot manager to an USB device and boot the computer system from that device to be able to test the boot manager. Make sure to select Do not change partitions IDs in step four of the boot manager creation.
When the test is going through without errors the boot manager can be installed on the primary partition or Master Boot Record. The software developers recommend to install the boot manager in the primary partition if possible.
The Windows Boot Manager Boot-US was tested on a Windows XP Service Pack 3 test system without difficulties.
Advertisement
















Yo Martin. duckduckgoing made me get to this link ;-) Seems a bit dated. I wonder how accurate would the guide be to dual boot openelec and windows 7 :)
Hi,
I am trying to use a Boot Manager and Norton GoBack. Is there any experience in that regard?
@Martin: Nice, thanks.
@Joshua: But those don’t yet come with any distro out of the box, so far as I know. I think that Ubuntu 8.10 (four more weeks) will have one, though.
@Dotan:
Well, there is GrubConf and QGRUBEditor for Linux. So yeah, there are applications for that.
Dotan yes it comes as a GUI and a command line utility and it can be configured directly in all versions of Windows since and including Windows 95.
> Windows because it is a Windows application
Does this mean that it can be configured from within Windows via a GUI? If so that is a great feature. I do not think that any Linux OS currently has a GUI for configuring the boot manager, though it is on the list of improvements to Ubuntu 8.10 (to be released next month).