South Korea's tech ambitions fueled by Samsung's $230B investment

Samsung plans to build five new chip plants in South Korea, committing $230B (300 trillion won) over the next 20 years.
In the past few years, chip manufacturing has become a serious issue due to supply chain disruption and other reasons. South Korea wants to prevent any future issues similar to recent years, and even though the crisis between the United States and China gets worse, two of the top-five biggest tech exporters in the world, it will still be able to match the demand and benefit from the situation financially.
The Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy of South Korea announced that the country is looking to become a superpower in the high-tech industry. It projects to invest $422B by 2026 to promote semiconductors, electric vehicle batteries, autonomous vehicles, robots, and displays. This move came a month later than the United States announcement of the Chips Act, offering billions for chipmakers that invest in the country.
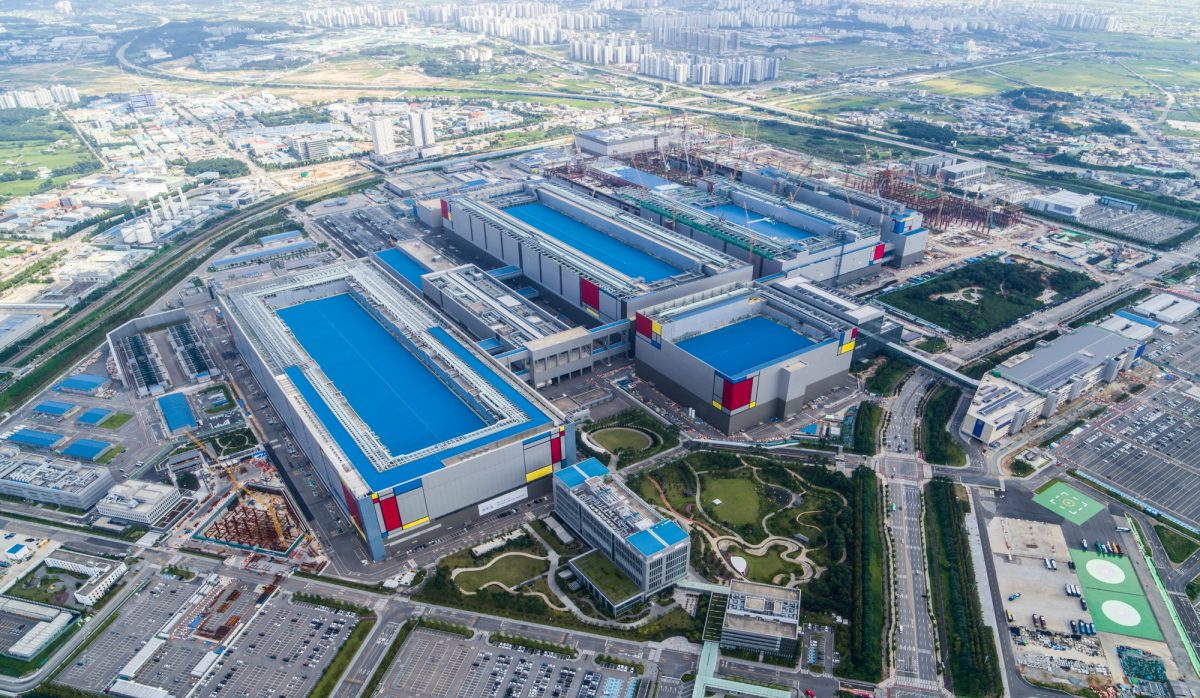

In January, the South Korean government raised the tax deduction rate for large companies for plant investments in chips and other strategic technologies from 8 percent to 15 percent. Apart from that, the government is looking for other ways to get more investments in the field. These new chip plants will also create job opportunities for people and probably lead the way to other investments and developments.
Tech Crunch reached out to a spokesperson of Samsung, and they said: "It is expected that we would invest about 300 trillion KRW ($230 billion) in the chip-making cluster through 2042." The governmental announcement says that five plants would be built in the next 20 years, but Samsung avoided to make any comments regarding the matter.
South Korea has two of the biggest memory chip makers in the world, Samsung and SK Hynix. With the upcoming projects, the country aims to expand its vision and play important roles in the non-memory chip market by improving its supply chain stability. Currently, the country aims to build a strong ecosystem and increase the domestic production rate to reduce dependence on specific countries.
Advertisement