Manage startup services in Linux with BUM
If you have ever had to change a service to either start or not start on a Linux machine, you know that process can be a little daunting. Not that it's impossible, but it's not always the simplest task. Fortunately there are plenty of tools available to make the process easier. One of those tools is Boot Up Manager (BUM). BUM is a graphical tool that allows you to select which services you want to run at startup. This can aid you in the process of getting the fastest boot time possible. Not only that, but there might well be processes running on your machine that you do not need. If you want to steamline your machine, you want this tool. Installation The installation of BUM is simple. You can install either through your Add/Remove Software tool or from the command line. To install from the command line follow these steps (I'll demonstrate using Ubuntu):
- Open up a terminal window.
- Issue the command
sudo apt-get install bum. - Type your sudo password and hit Enter.
- Accept any dependencies (if necessary).
Once the installation is complete, leave that terminal window open so you can start up the tool. Usage
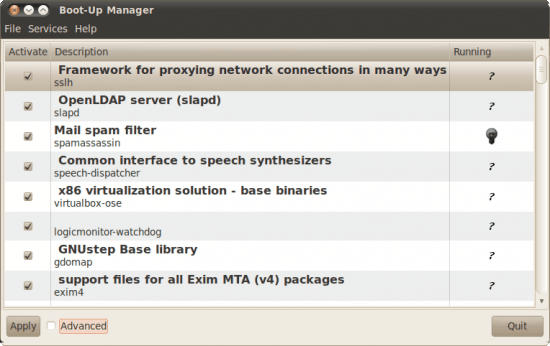
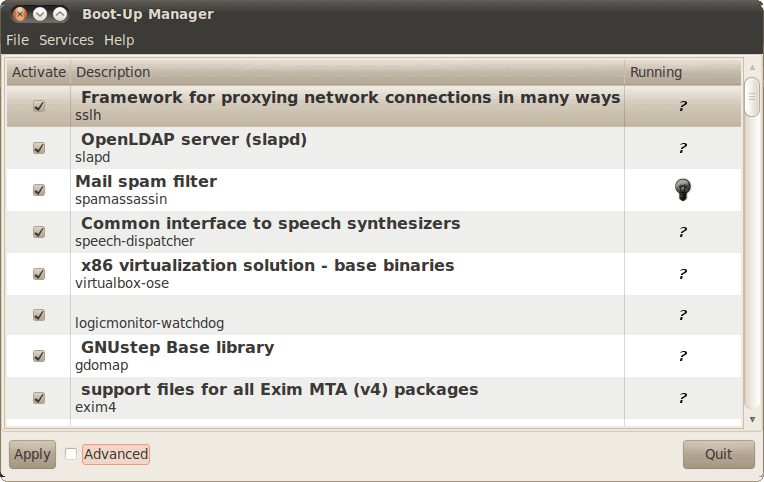
To fire up BUM issue the command sudo bum. I assume you have administrative rights. If you do not you will not be able to use this tool. When you have BUM up and running it will default in basic mode. In this window (see Figure 1) you can select which services you want to run by checking or unchecking the associated check box. If you make a change to a service  you have to click the Apply button to apply the change. But when you simply uncheck (or check) a box you are changing the startup status of the service. In other words, that status will only change upon the next boot of the machine. You can alter a services current status from with BUM by selecting  service and then clicking Services > Start or Services > Stop. Advanced mode As I said, by default BUM starts in basic mode. This mode offers one tab which is just a system summary mode, which is meant as an overview mode. The advanced mode The advanced mode can be selected by selecting the check box next to Advanced in the bottom left corner of the main window. When you toggle this mode you will see two new tabs:

Services: This allows you to manage system services on a per-runlevel basis. To change the priority of a service click on the Services tab, select a service, right click the service and change the priority in the resulting window (see Figure 2). You will need to have a fairly good understanding of process priority in order to make changes here. Startup Shutdown scripts: This tab should be left alone as editing in Run Level 5 (graphic mode) is not allowed. Legend You will notice icons associated with services that indicate their status. The icons are the following:
- A lit light bulb: This means the script has generated a service and is currently running.
- A dark light bulb: This means the script has generated a service but is not currently running.
- A dash: This means the script runs once at boot (to generate a configuration or such).
- A Question mark: BUM is not able to detect if the script is running.
Final thoughts If you have been looking for a tool to help you manage what services/processes are started on your machine, BUM is a solid candidate for this task.
Advertisement